Year :
2015
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
31 - 40 of 45 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 31. |
Make K the subject of the relation T = \(\sqrt{\frac{TK - H}{K - H}}\) A. K = \(\frac{H(T^2 - 1)}{T^2 - T}\) B. K = \(\frac{HT}{(T - 1)^2}\) C. K = \(\frac{H(T^2 + 1)}{T}\) D. K = \(\frac{H(T - 1)}{T}\) Detailed SolutionT = \(\sqrt{\frac{TK - H}{K - H}}\)Taking the square of both sides, give T2 = \(\frac{TK - H}{K - H}\) T2(K - H) = TK - H T2K - T2H = TK - H T2K - TK = T2H - H K(T2 - T) = H(T2 - 1) K = \(\frac{H(T^2 - 1)}{T^2 - T}\) |
|
| 32. |
Which of the following is used to determine the mode of a grouped data? A. Bar chart B. Frequency polygon C. Ogive D. Histogram |
D |
| 33. |
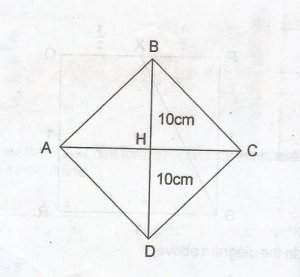
The area of a rhombus is 110 cm\(^2\). If the diagonals are 20 cm and (2x + 1) cm long, find the value of x. A. 5.0 B. 4.0 C. 3.0 D. 2.5 Detailed Solution
In the diagram,area of \(\Delta\)ABC is \(\frac{110}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x |AC| x |HB| 55 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x (2x + 1) x 10 55 = (2x + 1)5 55 = 10x + 5 55 - 5 = 10x 50 = 10x x = \(\frac{50}{10}\) = 5.0 |
|
| 34. |
Simplify: \(\frac{3x - y}{xy} - \frac{2x + 3y}{2xy} + \frac{1}{2}\) A. \(\frac{4x + 5y - xy}{2xy}\) B. \(\frac{5y - 4x + xy}{2xy}\) C. \(\frac{5x + 4y - xy}{2xy}\) D. \(\frac{4x - 5y + xy}{2xy}\) Detailed Solution\(\frac{3x - y}{xy} - \frac{2x + 3y}{2xy} + \frac{1}{2}\)= \(\frac{2(3x - y) - 1(2x + 3y) + xy}{2xy}\) = \(\frac{6x - 2y - 2x - 3y + xy}{2xy}\) = \(\frac{4x - 5y + xy}{2xy}\) |
|
| 35. |
A farmer uses \(\frac{2}{5}\) of his land to grow cassava, \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the remaining for yam and the rest for maize. Find the part of the land used for maize A. \(\frac{2}{15}\) B. \(\frac{2}{5}\) C. \(\frac{2}{3}\) D. \(\frac{4}{5}\) Detailed SolutionLet x represent the entire farmlandthen, \(\frac{2}{5}\)x + \(\frac{1}{3}\)[x - \(\frac{2}{3}x\)] + M = x Where M represents the part of the farmland used for growing maize, continuing \(\frac{2}{5}\)x + \(\frac{1}{3}\)x [1 - \(\frac{2}{3}x\)] + M = x \(\frac{2}{5}x + \frac{1}{3}\)x [\(\frac{3}{5}\)] + M = x \(\frac{2}{5}\)x + \(\frac{1x}{5}\) + M = x \(\frac{3x}{5} + M = x\) M = x - \(\frac{2}{5}\)x = x[1 - \(\frac{3}{5}\)] = x[\(\frac{2}{5}\)] = \(\frac{2x}{5}\) Hence the part of the land used for growing maize is & |
|
| 36. |
The rate of consumption of petrol by a vehicle varies directly as the square of the distance covered. If 4 litres of petrol is consumed on a distance of 15km. how far would the vehicle go on 9 litres of petrol? A. 22\(\frac{1}{2}\)km B. 30km C. 33\(\frac{1}{2}\)km D. 45km Detailed SolutionR \(\alpha\) D2R = D2K R = 4 Litres when D = 15cm thus; 4 = 152k 4 = 225k k = \(\frac{4}{225}\) This gives R = \(\frac{4D^2}{225}\) Where R = 9litres equation gives 9 = \(\frac{4D^2}{225}\) 9 x 225 = 4d2 D2 = \(\frac{9 \times 225}{4}\) D = \(\sqrt{9 \times 225}{4}\) = \(\frac{3 \times 15}{2}\) = 22\(\frac{1}{2}\)km |
|
| 37. |
A trader bought 100 oranges at 5 for N40.00 and 20 for N120.00. Find the profit or loss percent A. 20% profit B. 20% loss C. 25% profit D. 25% loss Detailed SolutionCost price CP of the 100 oranges = \(\frac{100}{5}\) x N40.00selling price SP of the 100 oranges = \(\frac{100}{20}\) x N120 = N600.00 so, profit or loss per cent = \(\frac{SP - CP}{CP}\) x 100% = \(\frac{600 - 800}{800}\) x 100% = \(\frac{-200}{800}\) x 100% Hence, loss per cent = 25% |
|
| 38. |
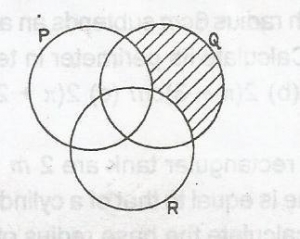 Describe the shaded portion in the diagram A. P' \(\cap\) Q \(\cap\) R' B. (P' \(\cap\) R)' \(\cap\) R C. P' \(\cap\) Q \(\cap\) R D. (P \(\cap\) Q)' \(\cap\) R |
A |
| 39. |
Find the value of p if \(\frac{1}{4}\)p + 3q = 10 and 2p - q = 7 A. 4 B. 3 C. -3 D. -4 Detailed Solution\(\frac{1}{4}\)p + 3p = 10...(1)2p - \(\frac{1}{3}\)q = 7...(2) Multiply equation (2) by 3 to clear fraction 3 x 2p - 3 x \(\frac{1}{3}\)q = 3 x 7 6p - q = 21 6p - 21 = q....(3) substituting 6p - 21 for q in (1) \(\frac{1}{4}\)p + 3(6p - 21) = 10...(4) Multiply equation (4) by 4 to clear fraction 4 x \(\frac{1}{4}\)p + 4 x 3(6p - 21) = 4 x 10 p + 12(6p - 21) = 40 p + 72p - 252 73p = 292 p = \(\frac{292}{73}\) = 4 |
|
| 40. |
Calculate the mean deviation of 5, 3, 0, 7, 2, 1 A. 0.0 B. 2.0 C. 2.5 D. 3.0 Detailed Solutionmean = \(\bar{x}\) = \(\frac{\sum x}{n}\)= \(\frac{5 + 3 + 0 + 7 + 2 + 1}{6}\) \(\frac{18}{6}\) = 3 \(\begin{array}{c|c} x & x - \bar{x} & |x - \bar{x}|\\ \hline 5 & -2 & 2 \\ \hline 3 & 0 & 0 \\ \hline 0 & -3 & 3 \\ \hline 7 & 4 & 4 \\ \hline 2 & -1 & 1 \\ \hline 1 & -2 & 2 \\ \hline & & & \sum|x - \bar{x}| \\ \hline & & & 12 \end{array}\) hence, MD = \(\frac{\sum|x - \bar{x}}{n}|\) \(\frac{12}{6}\) = 2 |
| 31. |
Make K the subject of the relation T = \(\sqrt{\frac{TK - H}{K - H}}\) A. K = \(\frac{H(T^2 - 1)}{T^2 - T}\) B. K = \(\frac{HT}{(T - 1)^2}\) C. K = \(\frac{H(T^2 + 1)}{T}\) D. K = \(\frac{H(T - 1)}{T}\) Detailed SolutionT = \(\sqrt{\frac{TK - H}{K - H}}\)Taking the square of both sides, give T2 = \(\frac{TK - H}{K - H}\) T2(K - H) = TK - H T2K - T2H = TK - H T2K - TK = T2H - H K(T2 - T) = H(T2 - 1) K = \(\frac{H(T^2 - 1)}{T^2 - T}\) |
|
| 32. |
Which of the following is used to determine the mode of a grouped data? A. Bar chart B. Frequency polygon C. Ogive D. Histogram |
D |
| 33. |
The area of a rhombus is 110 cm\(^2\). If the diagonals are 20 cm and (2x + 1) cm long, find the value of x. A. 5.0 B. 4.0 C. 3.0 D. 2.5 Detailed Solution
In the diagram,area of \(\Delta\)ABC is \(\frac{110}{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x |AC| x |HB| 55 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x (2x + 1) x 10 55 = (2x + 1)5 55 = 10x + 5 55 - 5 = 10x 50 = 10x x = \(\frac{50}{10}\) = 5.0 |
|
| 34. |
Simplify: \(\frac{3x - y}{xy} - \frac{2x + 3y}{2xy} + \frac{1}{2}\) A. \(\frac{4x + 5y - xy}{2xy}\) B. \(\frac{5y - 4x + xy}{2xy}\) C. \(\frac{5x + 4y - xy}{2xy}\) D. \(\frac{4x - 5y + xy}{2xy}\) Detailed Solution\(\frac{3x - y}{xy} - \frac{2x + 3y}{2xy} + \frac{1}{2}\)= \(\frac{2(3x - y) - 1(2x + 3y) + xy}{2xy}\) = \(\frac{6x - 2y - 2x - 3y + xy}{2xy}\) = \(\frac{4x - 5y + xy}{2xy}\) |
|
| 35. |
A farmer uses \(\frac{2}{5}\) of his land to grow cassava, \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the remaining for yam and the rest for maize. Find the part of the land used for maize A. \(\frac{2}{15}\) B. \(\frac{2}{5}\) C. \(\frac{2}{3}\) D. \(\frac{4}{5}\) Detailed SolutionLet x represent the entire farmlandthen, \(\frac{2}{5}\)x + \(\frac{1}{3}\)[x - \(\frac{2}{3}x\)] + M = x Where M represents the part of the farmland used for growing maize, continuing \(\frac{2}{5}\)x + \(\frac{1}{3}\)x [1 - \(\frac{2}{3}x\)] + M = x \(\frac{2}{5}x + \frac{1}{3}\)x [\(\frac{3}{5}\)] + M = x \(\frac{2}{5}\)x + \(\frac{1x}{5}\) + M = x \(\frac{3x}{5} + M = x\) M = x - \(\frac{2}{5}\)x = x[1 - \(\frac{3}{5}\)] = x[\(\frac{2}{5}\)] = \(\frac{2x}{5}\) Hence the part of the land used for growing maize is & |
| 36. |
The rate of consumption of petrol by a vehicle varies directly as the square of the distance covered. If 4 litres of petrol is consumed on a distance of 15km. how far would the vehicle go on 9 litres of petrol? A. 22\(\frac{1}{2}\)km B. 30km C. 33\(\frac{1}{2}\)km D. 45km Detailed SolutionR \(\alpha\) D2R = D2K R = 4 Litres when D = 15cm thus; 4 = 152k 4 = 225k k = \(\frac{4}{225}\) This gives R = \(\frac{4D^2}{225}\) Where R = 9litres equation gives 9 = \(\frac{4D^2}{225}\) 9 x 225 = 4d2 D2 = \(\frac{9 \times 225}{4}\) D = \(\sqrt{9 \times 225}{4}\) = \(\frac{3 \times 15}{2}\) = 22\(\frac{1}{2}\)km |
|
| 37. |
A trader bought 100 oranges at 5 for N40.00 and 20 for N120.00. Find the profit or loss percent A. 20% profit B. 20% loss C. 25% profit D. 25% loss Detailed SolutionCost price CP of the 100 oranges = \(\frac{100}{5}\) x N40.00selling price SP of the 100 oranges = \(\frac{100}{20}\) x N120 = N600.00 so, profit or loss per cent = \(\frac{SP - CP}{CP}\) x 100% = \(\frac{600 - 800}{800}\) x 100% = \(\frac{-200}{800}\) x 100% Hence, loss per cent = 25% |
|
| 38. |
 Describe the shaded portion in the diagram A. P' \(\cap\) Q \(\cap\) R' B. (P' \(\cap\) R)' \(\cap\) R C. P' \(\cap\) Q \(\cap\) R D. (P \(\cap\) Q)' \(\cap\) R |
A |
| 39. |
Find the value of p if \(\frac{1}{4}\)p + 3q = 10 and 2p - q = 7 A. 4 B. 3 C. -3 D. -4 Detailed Solution\(\frac{1}{4}\)p + 3p = 10...(1)2p - \(\frac{1}{3}\)q = 7...(2) Multiply equation (2) by 3 to clear fraction 3 x 2p - 3 x \(\frac{1}{3}\)q = 3 x 7 6p - q = 21 6p - 21 = q....(3) substituting 6p - 21 for q in (1) \(\frac{1}{4}\)p + 3(6p - 21) = 10...(4) Multiply equation (4) by 4 to clear fraction 4 x \(\frac{1}{4}\)p + 4 x 3(6p - 21) = 4 x 10 p + 12(6p - 21) = 40 p + 72p - 252 73p = 292 p = \(\frac{292}{73}\) = 4 |
|
| 40. |
Calculate the mean deviation of 5, 3, 0, 7, 2, 1 A. 0.0 B. 2.0 C. 2.5 D. 3.0 Detailed Solutionmean = \(\bar{x}\) = \(\frac{\sum x}{n}\)= \(\frac{5 + 3 + 0 + 7 + 2 + 1}{6}\) \(\frac{18}{6}\) = 3 \(\begin{array}{c|c} x & x - \bar{x} & |x - \bar{x}|\\ \hline 5 & -2 & 2 \\ \hline 3 & 0 & 0 \\ \hline 0 & -3 & 3 \\ \hline 7 & 4 & 4 \\ \hline 2 & -1 & 1 \\ \hline 1 & -2 & 2 \\ \hline & & & \sum|x - \bar{x}| \\ \hline & & & 12 \end{array}\) hence, MD = \(\frac{\sum|x - \bar{x}}{n}|\) \(\frac{12}{6}\) = 2 |