Year :
2015
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
21 - 30 of 45 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 21. |
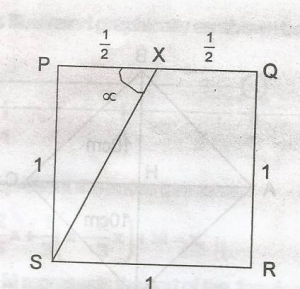
PQRT is square. If x is the midpoint of PQ, Calculate correct to the nearest degree, LPXS A. 53o B. 55o C. 63o D. 65o Detailed Solution
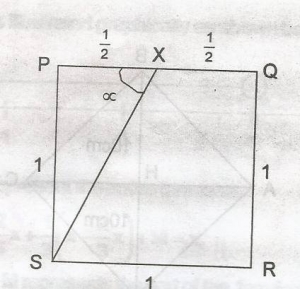 tan\(\alpha\) = \(\frac{1}{0.5}\) = 2 \(\alpha\) = tan - 1(2) = 63.43o = 63o |
|
| 22. |
The angle of elevation of an aircraft from a point K on the horizontal ground 30\(\alpha\). If the aircraft is 800m above the ground, how far is it from K? A. 400.00m B. 692.82m C. 923.76m D. 1,600.99m Detailed Solution
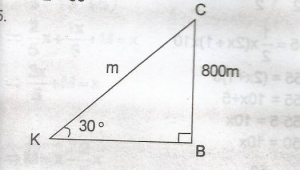 IKCL = \(\frac{800}{sin30^o}\) = \(\frac{800}{0.5}\) = 1600m |
|
| 23. |
The population of students in a school is 810. If this is represented on a pie chart, calculate the sectoral angle for a class of 7 students A. 32o B. 45o C. 60o D. 75o Detailed SolutionIn a school with students' population 810, the sectoral angle for a class of 7 students is= \(\frac{72}{810}\) x 360o = 32o |
|
| 24. |
The scores of twenty students in a test are as follows: 44, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 53, 54, 58, 59, 60, 61, 63, 65, 67, 70, 73, 75. Find the third quartile. A. 62 B. 63 C. 64 D. 65 Detailed SolutionThird quartile Q3 = \(\frac{3}{4}\)Nth= \(\frac{3}{4}\) x 20th score = 15th score = 63 |
|
| 25. |
\(\begin{array}{c|c} A. 5.6 B. 6.2 C. 6.6 D. 7.0 Detailed SolutionTo calculate the mean of grouped data,- First step to determine the midpoint (x) of each interval or class. 0 - 4 ►2 5 - 9 ► 7 10 - 14 ►12 These midpoints must then be multiplied by the frequencies of the corresponding classes: 2 X 2 = 4 1 X 7 = 7 2 X 12 = 24 Mean = ( 24 + 7 + 4) ÷ ( 2 + 1 + 2 ) : Mean = 7 |
|
| 26. |
The probability that kebba, Ebou and Omar will hit a target are \(\frac{2}{3}\), \(\frac{3}{4}\) and \(\frac{4}{5}\) respectively. Find the probability that only Kebba will hit the target. A. \(\frac{2}{5}\) B. \(\frac{7}{60}\) C. \(\frac{1}{30}\) D. \(\frac{1}{60}\) Detailed SolutionHence the probability that only Kebba will hit the target= P(K)xP(E')xP(O') = \(\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{1}{4} \times \frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{1}{30}\) |
|
| 27. |
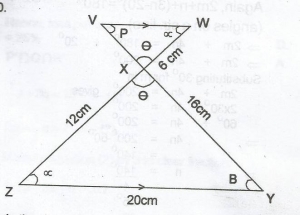
 In the diagram, VW//YZ, |WX| = 6cm, |XY| = 16cm, |YZ| = 20cm and |ZX| = 12cm. Calculate |VX| A. 3cm B. 4cm C. 6cm D. 8cm Detailed Solution
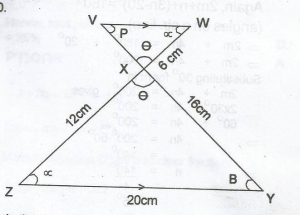 VX = \(\frac{16 \times 6}{12}\) = 8cm |
|
| 28. |
Tom will be 25 years old in n years' time. If he is 5 years younger than Bade's present age. A. (30 - n)years B. (20 - n)years C. (25 - n)years D. (30 + n)years Detailed SolutionLet Tom's present agr be x.Then x = 25 - n If Tom is 5 years younger than Bade, then Bade's present age is x + 5 = 25 - n + 5 = (30 - n) |
|
| 29. |
If \(\frac{\sqrt{2} + \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\) is simplified as m + n\(\sqrt{6}\), find the value of (m + n) A. \(\frac{1}{3}\) B. \(\frac{2}{3}\) C. 1\(\frac{1}{3}\) D. 1\(\frac{2}{3}\) Detailed Solution\(\frac{\sqrt{2} + \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{2} + \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\) x \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\)= \(\frac{\sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{3} + \sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{6} + 3}{3}\) = \(\frac{3 + \sqrt{6}}{3}\) = Hence, (m + n) = 1 + \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{3}\) |
|
| 30. |
 In the given diagram, \(\bar{QT}\) and \(\bar{PR}\) are straight lines, < ROS = (3n - 20), < SOT = n, < POL = m and < QOL is a right angle. Find the value of n. A. 35o B. 40o C. 55o D. 60o Detailed SolutionIn the diagram, QOR + 2m(vertically opposite angles)So, m + 90° + 2m = 180° (angles on str. line) 3m = 180° - 90° 3m = 90° m = \(\frac{90^o}{3}\) = 30° substituting 30° for m in 2m + 4n = 200° gives 2 x 30° + 4n = 200° 60° + 4n = 200° 4n = 200° - 60° = 140° n = \(\frac{140°}{4}\) < |
| 21. |
PQRT is square. If x is the midpoint of PQ, Calculate correct to the nearest degree, LPXS A. 53o B. 55o C. 63o D. 65o Detailed Solution
 tan\(\alpha\) = \(\frac{1}{0.5}\) = 2 \(\alpha\) = tan - 1(2) = 63.43o = 63o |
|
| 22. |
The angle of elevation of an aircraft from a point K on the horizontal ground 30\(\alpha\). If the aircraft is 800m above the ground, how far is it from K? A. 400.00m B. 692.82m C. 923.76m D. 1,600.99m Detailed Solution
 IKCL = \(\frac{800}{sin30^o}\) = \(\frac{800}{0.5}\) = 1600m |
|
| 23. |
The population of students in a school is 810. If this is represented on a pie chart, calculate the sectoral angle for a class of 7 students A. 32o B. 45o C. 60o D. 75o Detailed SolutionIn a school with students' population 810, the sectoral angle for a class of 7 students is= \(\frac{72}{810}\) x 360o = 32o |
|
| 24. |
The scores of twenty students in a test are as follows: 44, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 53, 54, 58, 59, 60, 61, 63, 65, 67, 70, 73, 75. Find the third quartile. A. 62 B. 63 C. 64 D. 65 Detailed SolutionThird quartile Q3 = \(\frac{3}{4}\)Nth= \(\frac{3}{4}\) x 20th score = 15th score = 63 |
|
| 25. |
\(\begin{array}{c|c} A. 5.6 B. 6.2 C. 6.6 D. 7.0 Detailed SolutionTo calculate the mean of grouped data,- First step to determine the midpoint (x) of each interval or class. 0 - 4 ►2 5 - 9 ► 7 10 - 14 ►12 These midpoints must then be multiplied by the frequencies of the corresponding classes: 2 X 2 = 4 1 X 7 = 7 2 X 12 = 24 Mean = ( 24 + 7 + 4) ÷ ( 2 + 1 + 2 ) : Mean = 7 |
| 26. |
The probability that kebba, Ebou and Omar will hit a target are \(\frac{2}{3}\), \(\frac{3}{4}\) and \(\frac{4}{5}\) respectively. Find the probability that only Kebba will hit the target. A. \(\frac{2}{5}\) B. \(\frac{7}{60}\) C. \(\frac{1}{30}\) D. \(\frac{1}{60}\) Detailed SolutionHence the probability that only Kebba will hit the target= P(K)xP(E')xP(O') = \(\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{1}{4} \times \frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{1}{30}\) |
|
| 27. |
 In the diagram, VW//YZ, |WX| = 6cm, |XY| = 16cm, |YZ| = 20cm and |ZX| = 12cm. Calculate |VX| A. 3cm B. 4cm C. 6cm D. 8cm Detailed Solution
 VX = \(\frac{16 \times 6}{12}\) = 8cm |
|
| 28. |
Tom will be 25 years old in n years' time. If he is 5 years younger than Bade's present age. A. (30 - n)years B. (20 - n)years C. (25 - n)years D. (30 + n)years Detailed SolutionLet Tom's present agr be x.Then x = 25 - n If Tom is 5 years younger than Bade, then Bade's present age is x + 5 = 25 - n + 5 = (30 - n) |
|
| 29. |
If \(\frac{\sqrt{2} + \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\) is simplified as m + n\(\sqrt{6}\), find the value of (m + n) A. \(\frac{1}{3}\) B. \(\frac{2}{3}\) C. 1\(\frac{1}{3}\) D. 1\(\frac{2}{3}\) Detailed Solution\(\frac{\sqrt{2} + \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{2} + \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\) x \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\)= \(\frac{\sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{3} + \sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{3}}\) = \(\frac{\sqrt{6} + 3}{3}\) = \(\frac{3 + \sqrt{6}}{3}\) = Hence, (m + n) = 1 + \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 1\(\frac{1}{3}\) |
|
| 30. |
 In the given diagram, \(\bar{QT}\) and \(\bar{PR}\) are straight lines, < ROS = (3n - 20), < SOT = n, < POL = m and < QOL is a right angle. Find the value of n. A. 35o B. 40o C. 55o D. 60o Detailed SolutionIn the diagram, QOR + 2m(vertically opposite angles)So, m + 90° + 2m = 180° (angles on str. line) 3m = 180° - 90° 3m = 90° m = \(\frac{90^o}{3}\) = 30° substituting 30° for m in 2m + 4n = 200° gives 2 x 30° + 4n = 200° 60° + 4n = 200° 4n = 200° - 60° = 140° n = \(\frac{140°}{4}\) < |