Year :
2018
Title :
Chemistry
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
11 - 20 of 50 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 11. |
Ethene is produced from ethanol by A. decomposition B. hydrolysis C. ozonolysis D. dehydration Detailed SolutionEthene can be gotten from the dehydration of ethanol in the presence of excess \(H_{2}SO_{4}\) or \(H_{3}PO_{4}\). |
|
| 12. |
Consider the following equilibrium reaction: \(2AB_{{2}{(g)}} + B_{{2}{(g)}} \to 2AB_{{3}{(g)}}\). \(\Delta H= -X kJmol^{-1}\). The backward reaction will be favored by A. a decrease in pressure B. an increase in pressure C. a decrease in temperature D. an introduction of a positive catalyst Detailed SolutionThe equilibrium position is shifted to the left with a decrease in pressure in this system because the number of gaseous molecules on the right is less. (Le-Chatelier's principle). |
|
| 13. |
What is the mass of solute in 500\(cm^{3}\) of 0.005\(moldm^{-3}\) \(H_{2}SO_{4}\)? ( H = 1, S = 32.0, O=16.0) A. 0.490g B. 0.049g C. 0.245g D. 0.0245g Detailed Solution\(500cm^{3} = 0.005moldm^{-3}\)\(1000cm^{3} = \frac{0.005}{500} \times 1000cm^{3} = 0.010moldm^{-3}\) Molar concentration = \(\frac{mass in gdm^{-3}}{molar mass in gmol^{-1}}\) \(0.01moldm^{-3} = \frac{mass in gdm^{-3}}{98.0gmol^{-1}}\) (Molar mass of \(H_{2}SO_{4}\) = (2x1) + 32 + (16x4) = 98) \(mass in gdm^{-3} = 0.980gdm^{-3}\) \(1000cm^{3} = 0.980g\) \(500cm^{3} = \frac{0.980}{1000} \times 500 = 0.490g\) |
|
| 14. |
Pure water can be made to boil at a temperature lower than 100°C by A. reducing its quantity B. decreasing the external pressure C. distilling it D. increasing the external pressure Detailed SolutionThe easiest and most drastic way to change the boiling point is by tampering with the pressure above your water. To lower the boiling point, you need simply to decrease its external pressure. |
|
| 15. |
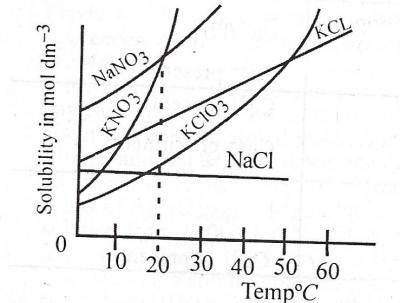 At what temperature does the solubility of \(KNO_{3}\) equal that of \(NaNO_{3}\)? A. 0°C B. 20°C C. 30°C D. 40°C Detailed SolutionFrom the graph, check for their point of intersection and trace it down to the temperature axis. |
|
| 16. |
When a salt is added to its saturated solution, the salt A. dissolves and the solution becomes super saturated B. dissolves and the solution becomes unsaturated C. precipitates and the solution remains unchanged D. dissolves and crystals are formed Detailed SolutionThe point of saturation is the point it gets to and from thence, the solution can no longer take in the salt anymore. From this point, it begins to form precipitate while the solution remains unchanged. |
|
| 17. |
When substance X was added to a solution of bromine water, the solution became colourless. X is likely to be A. propane B. propanoic acid C. propyne D. propanol Detailed SolutionThus bromine water will be decolorized by alkynes due to the presence of two pi bonds available for reaction! |
|
| 18. |
The preferential discharge of ions during electrolysis is influenced by the A. mechanism of electrolysis B. electrolytic reactions C. nature of the electrode D. type of electrolytic cell Detailed SolutionThe preferential discharge of ions is influenced by:- The position of the ions in the electrochemical series - The concentration of the ions in the electrolyte - The nature of the electrode |
|
| 19. |
The valence electrons of \(_{12}Mg\) are in the A. 3s orbital B. 2p\(_{x}\) C. 2s orbital D. 1s orbital Detailed Solution\(_{12}Mg = 2, 8, 2\)\(= 1s^{2} 2s^{2} 2p^{6} 3s^{2}\) |
|
| 20. |
Stainless steel is an alloy comprising of A. Fe and C B. Fe and Ni C. Fe, C and Ni D. Fe, C and Al Detailed SolutionStainless steel comprises iron (Fe), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), silicon (Si), carbon (C) and, in many cases, significant amounts of nickel (Ni) and molybdenum (Mo). |
| 11. |
Ethene is produced from ethanol by A. decomposition B. hydrolysis C. ozonolysis D. dehydration Detailed SolutionEthene can be gotten from the dehydration of ethanol in the presence of excess \(H_{2}SO_{4}\) or \(H_{3}PO_{4}\). |
|
| 12. |
Consider the following equilibrium reaction: \(2AB_{{2}{(g)}} + B_{{2}{(g)}} \to 2AB_{{3}{(g)}}\). \(\Delta H= -X kJmol^{-1}\). The backward reaction will be favored by A. a decrease in pressure B. an increase in pressure C. a decrease in temperature D. an introduction of a positive catalyst Detailed SolutionThe equilibrium position is shifted to the left with a decrease in pressure in this system because the number of gaseous molecules on the right is less. (Le-Chatelier's principle). |
|
| 13. |
What is the mass of solute in 500\(cm^{3}\) of 0.005\(moldm^{-3}\) \(H_{2}SO_{4}\)? ( H = 1, S = 32.0, O=16.0) A. 0.490g B. 0.049g C. 0.245g D. 0.0245g Detailed Solution\(500cm^{3} = 0.005moldm^{-3}\)\(1000cm^{3} = \frac{0.005}{500} \times 1000cm^{3} = 0.010moldm^{-3}\) Molar concentration = \(\frac{mass in gdm^{-3}}{molar mass in gmol^{-1}}\) \(0.01moldm^{-3} = \frac{mass in gdm^{-3}}{98.0gmol^{-1}}\) (Molar mass of \(H_{2}SO_{4}\) = (2x1) + 32 + (16x4) = 98) \(mass in gdm^{-3} = 0.980gdm^{-3}\) \(1000cm^{3} = 0.980g\) \(500cm^{3} = \frac{0.980}{1000} \times 500 = 0.490g\) |
|
| 14. |
Pure water can be made to boil at a temperature lower than 100°C by A. reducing its quantity B. decreasing the external pressure C. distilling it D. increasing the external pressure Detailed SolutionThe easiest and most drastic way to change the boiling point is by tampering with the pressure above your water. To lower the boiling point, you need simply to decrease its external pressure. |
|
| 15. |
 At what temperature does the solubility of \(KNO_{3}\) equal that of \(NaNO_{3}\)? A. 0°C B. 20°C C. 30°C D. 40°C Detailed SolutionFrom the graph, check for their point of intersection and trace it down to the temperature axis. |
| 16. |
When a salt is added to its saturated solution, the salt A. dissolves and the solution becomes super saturated B. dissolves and the solution becomes unsaturated C. precipitates and the solution remains unchanged D. dissolves and crystals are formed Detailed SolutionThe point of saturation is the point it gets to and from thence, the solution can no longer take in the salt anymore. From this point, it begins to form precipitate while the solution remains unchanged. |
|
| 17. |
When substance X was added to a solution of bromine water, the solution became colourless. X is likely to be A. propane B. propanoic acid C. propyne D. propanol Detailed SolutionThus bromine water will be decolorized by alkynes due to the presence of two pi bonds available for reaction! |
|
| 18. |
The preferential discharge of ions during electrolysis is influenced by the A. mechanism of electrolysis B. electrolytic reactions C. nature of the electrode D. type of electrolytic cell Detailed SolutionThe preferential discharge of ions is influenced by:- The position of the ions in the electrochemical series - The concentration of the ions in the electrolyte - The nature of the electrode |
|
| 19. |
The valence electrons of \(_{12}Mg\) are in the A. 3s orbital B. 2p\(_{x}\) C. 2s orbital D. 1s orbital Detailed Solution\(_{12}Mg = 2, 8, 2\)\(= 1s^{2} 2s^{2} 2p^{6} 3s^{2}\) |
|
| 20. |
Stainless steel is an alloy comprising of A. Fe and C B. Fe and Ni C. Fe, C and Ni D. Fe, C and Al Detailed SolutionStainless steel comprises iron (Fe), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), silicon (Si), carbon (C) and, in many cases, significant amounts of nickel (Ni) and molybdenum (Mo). |