Year :
2002
Title :
Mathematics (Core)
Exam :
WASSCE/WAEC MAY/JUNE
Paper 1 | Objectives
31 - 40 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 31. |
Simplify \(\frac{2^{\frac{1}{2}}\times 8^{\frac{1}{2}}}{4}\) A. 1 B. 2 C. 4 D. 16 Detailed Solution\(\frac{2^{\frac{1}{2}}\times 8^{\frac{1}{2}}}{4}\\=\frac{2^{\frac{1}{2}}\times 2^{\frac{3}{2}}}{2^2}\\=2^{\frac{1}{2}}+2^{\frac{3}{2}}-2=2^0 = 1\) |
|
| 32. |
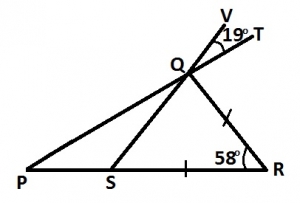 In the diagram, |SR| = |RQ| and ∠PRQ = 58o ∠VQT = 19o, PQT, SQV and PSR are straight lines. Find ∠QPS A. 42o B. 39o C. 38o D. 30o |
A |
| 33. |
The angle of depression of a point Q from a vertical tower PR, 30m high, is 40°. If the foot P of the tower is on the same horizontal level as Q, find, correct to 2 decimal places, |PQ|. A. 35.75m B. 25.00m C. 22.98m D. 19.28 Detailed Solution \(\tan 40° = \frac{30}{|PQ|}\) \(|PQ| = \frac{30}{\tan 40°} = \frac{30}{0.839}\) = 35.75m |
|
| 34. |
The volume of a cylinder of radius 14cm is 210cm3. What is the curved surface area of the cylinder? A. 15cm2 B. 30cm2 C. 616cm2 D. 1262cm2 Detailed Solution\(V = \pi r^2 h\\210 = \frac{22}{7} \times 14^2 \times h \\ h = \frac{210}{22 \times 28}\) Curved surface area \(= 2r\pi h\\ = 2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 14 \times \frac{210}{22 \times 26} = 30cm^2\) |
|
| 35. |
Simplify \(3\sqrt{12} + 10\sqrt{3} - \frac{6}{\sqrt{3}}\) A. \(7\sqrt{3}\) B. \(10\sqrt{3}\) C. \(14\sqrt{3}\) D. \(18\sqrt{3}\) Detailed Solution\(3\sqrt{12} + 10\sqrt{3} - \frac{6}{\sqrt{3}}\)= \(3(\sqrt{4 \times 3}) + 10\sqrt{3} - (\frac{6}{\sqrt{3}})(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}})\) = \(6\sqrt{3} + 10\sqrt{3} - 2\sqrt{3}\) = \(14\sqrt{3}\) |
|
| 36. |
Factorize m(2a-b)-2n(b-2a) A. (2a-b)(2n-m) B. (2a+b)(m-2n) C. (2a-b)(m+2n) D. (2a-b)(m-2n) Detailed Solutionm(2a - b) - 2n(b - 2a)= m(2a - b) - (-2n)(2a - b) = m(2a - b) + 2n(2a - b) = (m + 2n)(2a - b) |
|
| 37. |
If q oranges are sold for t Naira, how many oranges can be bought for p naira? A. \(\frac{p}{2}t\) B. \(\frac{qt}{p}\) C. \(\frac{q}{pt}\) D. \(\frac{pq}{t}\) Detailed Solutionq oranges = t naira1 naira = \(\frac{q}{t}\) p naira = \(p(\frac{q}{t})\) = \(\frac{pq}{t}\) oranges |
|
| 38. |
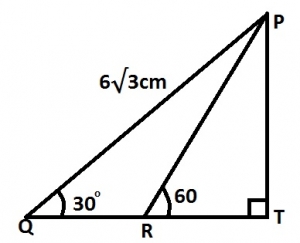 In the diagram, QRT is a straight line. If angle PTR = 90°, angle PRT = 60°, angle PQR = 30° and |PQ| = \(6\sqrt{3}cm\), calculate |RT| A. 0.3cm B. \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}cm\) C. 3cm D. \(3\sqrt{3}cm\) Detailed SolutionIn \(\Delta\) QPT,\(\frac{PT}{6\sqrt{3}} = \sin 30°\) PT = \(6\sqrt{3} \times \frac{1}{2} = 3\sqrt{3} cm\) In \(\Delta\) RPT, \(\frac{PT}{RT} = \tan 60°\) \(\frac{3\sqrt{3}}{RT} = \tan 60°\) \(RT = \frac{3\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = 3 cm\) |
|
| 39. |
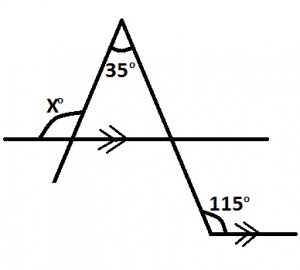 In the diagram, calculate the value of x A. 35o B. 80o C. 100o D. 115o Detailed Solution x - 35° = 65° (corresponding angles) x = 65° + 35° = 100° |
|
| 40. |
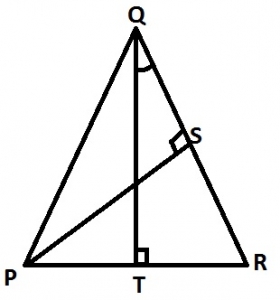 In the diagram, \(\bar{PS}\hspace{1mm} and \hspace{1mm}\bar{QT}\) are two altitudes of ∆PQR. Which of the following is equal to ∠RQT? A. ∠PQT B. ∠SRP C. ∠PQR D. ∠SPR |
D |
| 31. |
Simplify \(\frac{2^{\frac{1}{2}}\times 8^{\frac{1}{2}}}{4}\) A. 1 B. 2 C. 4 D. 16 Detailed Solution\(\frac{2^{\frac{1}{2}}\times 8^{\frac{1}{2}}}{4}\\=\frac{2^{\frac{1}{2}}\times 2^{\frac{3}{2}}}{2^2}\\=2^{\frac{1}{2}}+2^{\frac{3}{2}}-2=2^0 = 1\) |
|
| 32. |
 In the diagram, |SR| = |RQ| and ∠PRQ = 58o ∠VQT = 19o, PQT, SQV and PSR are straight lines. Find ∠QPS A. 42o B. 39o C. 38o D. 30o |
A |
| 33. |
The angle of depression of a point Q from a vertical tower PR, 30m high, is 40°. If the foot P of the tower is on the same horizontal level as Q, find, correct to 2 decimal places, |PQ|. A. 35.75m B. 25.00m C. 22.98m D. 19.28 Detailed Solution \(\tan 40° = \frac{30}{|PQ|}\) \(|PQ| = \frac{30}{\tan 40°} = \frac{30}{0.839}\) = 35.75m |
|
| 34. |
The volume of a cylinder of radius 14cm is 210cm3. What is the curved surface area of the cylinder? A. 15cm2 B. 30cm2 C. 616cm2 D. 1262cm2 Detailed Solution\(V = \pi r^2 h\\210 = \frac{22}{7} \times 14^2 \times h \\ h = \frac{210}{22 \times 28}\) Curved surface area \(= 2r\pi h\\ = 2 \times \frac{22}{7} \times 14 \times \frac{210}{22 \times 26} = 30cm^2\) |
|
| 35. |
Simplify \(3\sqrt{12} + 10\sqrt{3} - \frac{6}{\sqrt{3}}\) A. \(7\sqrt{3}\) B. \(10\sqrt{3}\) C. \(14\sqrt{3}\) D. \(18\sqrt{3}\) Detailed Solution\(3\sqrt{12} + 10\sqrt{3} - \frac{6}{\sqrt{3}}\)= \(3(\sqrt{4 \times 3}) + 10\sqrt{3} - (\frac{6}{\sqrt{3}})(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}})\) = \(6\sqrt{3} + 10\sqrt{3} - 2\sqrt{3}\) = \(14\sqrt{3}\) |
| 36. |
Factorize m(2a-b)-2n(b-2a) A. (2a-b)(2n-m) B. (2a+b)(m-2n) C. (2a-b)(m+2n) D. (2a-b)(m-2n) Detailed Solutionm(2a - b) - 2n(b - 2a)= m(2a - b) - (-2n)(2a - b) = m(2a - b) + 2n(2a - b) = (m + 2n)(2a - b) |
|
| 37. |
If q oranges are sold for t Naira, how many oranges can be bought for p naira? A. \(\frac{p}{2}t\) B. \(\frac{qt}{p}\) C. \(\frac{q}{pt}\) D. \(\frac{pq}{t}\) Detailed Solutionq oranges = t naira1 naira = \(\frac{q}{t}\) p naira = \(p(\frac{q}{t})\) = \(\frac{pq}{t}\) oranges |
|
| 38. |
 In the diagram, QRT is a straight line. If angle PTR = 90°, angle PRT = 60°, angle PQR = 30° and |PQ| = \(6\sqrt{3}cm\), calculate |RT| A. 0.3cm B. \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}cm\) C. 3cm D. \(3\sqrt{3}cm\) Detailed SolutionIn \(\Delta\) QPT,\(\frac{PT}{6\sqrt{3}} = \sin 30°\) PT = \(6\sqrt{3} \times \frac{1}{2} = 3\sqrt{3} cm\) In \(\Delta\) RPT, \(\frac{PT}{RT} = \tan 60°\) \(\frac{3\sqrt{3}}{RT} = \tan 60°\) \(RT = \frac{3\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = 3 cm\) |
|
| 39. |
 In the diagram, calculate the value of x A. 35o B. 80o C. 100o D. 115o Detailed Solution x - 35° = 65° (corresponding angles) x = 65° + 35° = 100° |
|
| 40. |
 In the diagram, \(\bar{PS}\hspace{1mm} and \hspace{1mm}\bar{QT}\) are two altitudes of ∆PQR. Which of the following is equal to ∠RQT? A. ∠PQT B. ∠SRP C. ∠PQR D. ∠SPR |
D |