Year :
2013
Title :
Agric Science
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
31 - 40 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 31. |
The causative organism of Avian influenza is a A. bacterium B. virus C. fungus D. protozoan. |
B |
| 32. |
The introduction of proper planktons species A. fertilization B. innoculation C. stocking D. liming. |
B |
| 33. |
Selection based on the performance of ancestors A. family selection B. pedigree selection C. progeny selection D. line selection. |
B |
| 34. |
The most important of all the factors of A. labour B. capital C. land D. management. |
C |
| 35. |
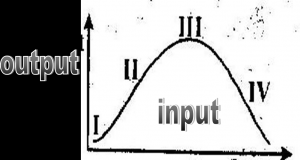 From the curve above, at what point is it A. I B. II C. III D. IV |
C |
| 36. |
Elastic demand is the type in which a change in A. brings about greater change in quantity of goods demanded B. of a commodity leads to little or no change in demand C. leads to equal change in commodity demanded D. may not change the demand of quantity of commodity. Detailed Solutionelastic demand is The variation in demand in response to a variation in price. It may also be defined as the ratio of the percentage change in demand to the percentage change in price of particular commodity. (when the change in price of a commodity, also leads to an equal change in quantity demanded.) |
|
| 37. |
Farm labour is usually measured in terms of A. amount of wages paid to labour B. hours or days of work by labour C. level of education of labour D. type of work done by labour. |
B |
| 38. |
A piece of information contained in payroll A. date of employment B. equity C. income generated D. total credit. |
A |
| 39. |
Retailers may create artificial scarcity of goods A. price hiking B. hoarding C. under producing D. processing. |
B |
| 40. |
The most effective method of disseminating A. individual method B. group method C. mass method D. cooperative method |
C |
| 31. |
The causative organism of Avian influenza is a A. bacterium B. virus C. fungus D. protozoan. |
B |
| 32. |
The introduction of proper planktons species A. fertilization B. innoculation C. stocking D. liming. |
B |
| 33. |
Selection based on the performance of ancestors A. family selection B. pedigree selection C. progeny selection D. line selection. |
B |
| 34. |
The most important of all the factors of A. labour B. capital C. land D. management. |
C |
| 35. |
 From the curve above, at what point is it A. I B. II C. III D. IV |
C |
| 36. |
Elastic demand is the type in which a change in A. brings about greater change in quantity of goods demanded B. of a commodity leads to little or no change in demand C. leads to equal change in commodity demanded D. may not change the demand of quantity of commodity. Detailed Solutionelastic demand is The variation in demand in response to a variation in price. It may also be defined as the ratio of the percentage change in demand to the percentage change in price of particular commodity. (when the change in price of a commodity, also leads to an equal change in quantity demanded.) |
|
| 37. |
Farm labour is usually measured in terms of A. amount of wages paid to labour B. hours or days of work by labour C. level of education of labour D. type of work done by labour. |
B |
| 38. |
A piece of information contained in payroll A. date of employment B. equity C. income generated D. total credit. |
A |
| 39. |
Retailers may create artificial scarcity of goods A. price hiking B. hoarding C. under producing D. processing. |
B |
| 40. |
The most effective method of disseminating A. individual method B. group method C. mass method D. cooperative method |
C |