Year :
1989
Title :
Chemistry
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
41 - 49 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 41. |
 In the above set up substances X and Y are respectively A. lime water copper (ll) tetraoxosulphate (lV) B. potassium trioxocarbonate and alkaline pyrogallol C. potassium hydroxide and alkaline pyrogallol D. potassium trioxocarbonate (lV) and concentrated tetraoxosulphate (IV) acid |
C |
| 42. |
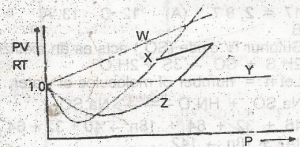 Which of the curves in the above graph illustrates the behaviour of an ideal gas? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z |
C |
| 43. |
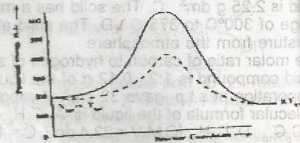 The above diagram gives the potential energy profile of the catalyst and uncatalysed reactions of X(g) + Y(g) → XY(g). Deduce the respective activation energies in KJ of the catalysed and uncatalysed reverse reactions: XY(g) → X(g) + Y(g) A. 300, 500 B. 500, 300 C. -300, -500 D. -500, -300 |
A |
| 44. |
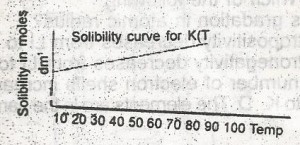 If in the graph above 1 dm 3 of a saturated solution of KCL is cooled from 80oC, the mass of crystals deposited will be A. 7.45 g B. 14.90 g C. 74.50 g D. 149.00 g |
D |
| 45. |
 The above graph shows a typical heating curve from the solid phase through the liquid phase to the gaseous phase of a substance. Which part of the curve shows solid and liquid in equilibrium? A. T B. U C. X D. Y |
A |
| 46. |
 Which of the following compounds is an isomer of the compound A. A B. B C. C D. D |
D |
| 47. |
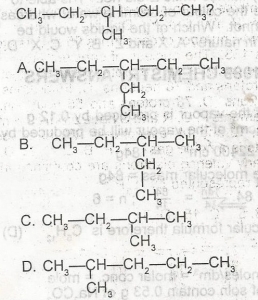 Which of the following is NOT a monomer? A. A B. B C. C D. D |
A |
| 48. |
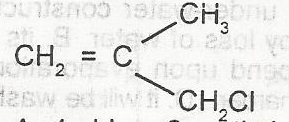 What is the IUPAC name for the compound A. 1-chloro-2-methylprop-2,3-ene B. 1-chloro-2-methylprop-2-ene C. 3-chloro-2-methylprop-1-ene D. 3-chloro-2methylprop-1,2-ene |
C |
| 49. |
COg + H2Og \(\to\) 2g + H2g \(\Delta\)H = -4100J. Which of the following factors favour the formation of hydrogen in the above reaction? i. high pressure. ii. low pressure iii. high temperature iv. use of excess steam A. i, iii and iv B. iii only C. ii, iii and i D. iv only |
D |
| 41. |
 In the above set up substances X and Y are respectively A. lime water copper (ll) tetraoxosulphate (lV) B. potassium trioxocarbonate and alkaline pyrogallol C. potassium hydroxide and alkaline pyrogallol D. potassium trioxocarbonate (lV) and concentrated tetraoxosulphate (IV) acid |
C |
| 42. |
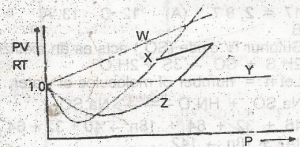 Which of the curves in the above graph illustrates the behaviour of an ideal gas? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z |
C |
| 43. |
 The above diagram gives the potential energy profile of the catalyst and uncatalysed reactions of X(g) + Y(g) → XY(g). Deduce the respective activation energies in KJ of the catalysed and uncatalysed reverse reactions: XY(g) → X(g) + Y(g) A. 300, 500 B. 500, 300 C. -300, -500 D. -500, -300 |
A |
| 44. |
 If in the graph above 1 dm 3 of a saturated solution of KCL is cooled from 80oC, the mass of crystals deposited will be A. 7.45 g B. 14.90 g C. 74.50 g D. 149.00 g |
D |
| 45. |
 The above graph shows a typical heating curve from the solid phase through the liquid phase to the gaseous phase of a substance. Which part of the curve shows solid and liquid in equilibrium? A. T B. U C. X D. Y |
A |
| 46. |
 Which of the following compounds is an isomer of the compound A. A B. B C. C D. D |
D |
| 47. |
 Which of the following is NOT a monomer? A. A B. B C. C D. D |
A |
| 48. |
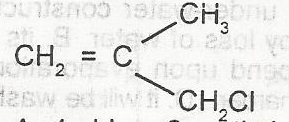 What is the IUPAC name for the compound A. 1-chloro-2-methylprop-2,3-ene B. 1-chloro-2-methylprop-2-ene C. 3-chloro-2-methylprop-1-ene D. 3-chloro-2methylprop-1,2-ene |
C |
| 49. |
COg + H2Og \(\to\) 2g + H2g \(\Delta\)H = -4100J. Which of the following factors favour the formation of hydrogen in the above reaction? i. high pressure. ii. low pressure iii. high temperature iv. use of excess steam A. i, iii and iv B. iii only C. ii, iii and i D. iv only |
D |