Year :
1997
Title :
Biology
Exam :
JAMB Exam
Paper 1 | Objectives
31 - 40 of 49 Questions
| # | Question | Ans |
|---|---|---|
| 31. |
The part of the brain that regulates most biological cycles in humans is A. olfactory lobe B. optic lobe C. medulla oblongata D. pineal body Detailed Solutionthe medulla oblongata is a portion of the hindbrain that controls autonomic (nervous system) functions in humans. |
|
| 32. |
The ability of the eye to focus on both near and distant objects is termed A. image formation B. refraction C. hypermetropia D. Accomodation |
D |
| 33. |
The speed of wind can be measured with an instrument called A. hygrometer B. secchi disc C. anemometer D. wind vane |
C |
| 34. |
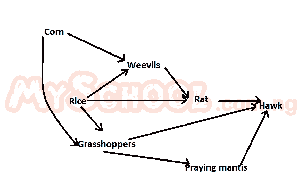 Which organism in the food-web illustrated above is an omnivore? A. Weevils B. Rat C. Hawk D. Prayer mantis |
B |
| 35. |
Toads and lizards in an ecosystem depend on a limited quantity of food. This is an example of A. parasitism B. intraspecific competition C. predation D. interspecific competition |
D |
| 36. |
Adaptive features of plants to desert conditions include? A. thick barks, succulent stems and sunken stomata B. thin barks, succulent stems and sunken stomata C. thin barks, air floats on stems and sunken stomata D. air spaces in tissues, adventitious roots and thick barks Detailed SolutionThe leaves and stems of many desert plants have a thick, waxy covering.This waxy substance does not cover the stomata, but it covers most of the leaves, keeping the plants cooler and reducing evaporative loss. Small leaves on desert plants also help reduce moisture loss during transpiration. Eg cactus plants: · thick, waxy skin to reduce loss of water and to reflect heat · large, fleshy stems to store water · thorns and thin, spiky or glossy leave |
|
| 37. |
The Southern Guinea Savanna differs from the Northern Guinea Savanna in that it has A. lower rainfall and shorter grasses B. less grasses and scattered trees C. more rainfall and taller grasses D. less arboreal and burrowing animals |
C |
| 38. |
After a heavy rainfall and the formation of a large pond, the most likely sequence of changes in the vegetation of the pond is A. Euglena → water lily → Spirogyra → grass B. water lily → Spirogyra →grass → Euglena C. Spirogyra → Euglena → grass → water lily D. Euglena → Spirogyra → water lily → grass |
C |
| 39. |
In a soil sample, the relative amouunts of the different soil particles can best be determined by the process of A. filtration B. centrifugation C. precipitation D. sedimentation |
D |
| 40. |
Which is the most important pollutant of the marine environment in Nigeria? A. Insecticides B. Sewage C. Oil D. Inorganic fertilizers |
C |
| 31. |
The part of the brain that regulates most biological cycles in humans is A. olfactory lobe B. optic lobe C. medulla oblongata D. pineal body Detailed Solutionthe medulla oblongata is a portion of the hindbrain that controls autonomic (nervous system) functions in humans. |
|
| 32. |
The ability of the eye to focus on both near and distant objects is termed A. image formation B. refraction C. hypermetropia D. Accomodation |
D |
| 33. |
The speed of wind can be measured with an instrument called A. hygrometer B. secchi disc C. anemometer D. wind vane |
C |
| 34. |
 Which organism in the food-web illustrated above is an omnivore? A. Weevils B. Rat C. Hawk D. Prayer mantis |
B |
| 35. |
Toads and lizards in an ecosystem depend on a limited quantity of food. This is an example of A. parasitism B. intraspecific competition C. predation D. interspecific competition |
D |
| 36. |
Adaptive features of plants to desert conditions include? A. thick barks, succulent stems and sunken stomata B. thin barks, succulent stems and sunken stomata C. thin barks, air floats on stems and sunken stomata D. air spaces in tissues, adventitious roots and thick barks Detailed SolutionThe leaves and stems of many desert plants have a thick, waxy covering.This waxy substance does not cover the stomata, but it covers most of the leaves, keeping the plants cooler and reducing evaporative loss. Small leaves on desert plants also help reduce moisture loss during transpiration. Eg cactus plants: · thick, waxy skin to reduce loss of water and to reflect heat · large, fleshy stems to store water · thorns and thin, spiky or glossy leave |
|
| 37. |
The Southern Guinea Savanna differs from the Northern Guinea Savanna in that it has A. lower rainfall and shorter grasses B. less grasses and scattered trees C. more rainfall and taller grasses D. less arboreal and burrowing animals |
C |
| 38. |
After a heavy rainfall and the formation of a large pond, the most likely sequence of changes in the vegetation of the pond is A. Euglena → water lily → Spirogyra → grass B. water lily → Spirogyra →grass → Euglena C. Spirogyra → Euglena → grass → water lily D. Euglena → Spirogyra → water lily → grass |
C |
| 39. |
In a soil sample, the relative amouunts of the different soil particles can best be determined by the process of A. filtration B. centrifugation C. precipitation D. sedimentation |
D |
| 40. |
Which is the most important pollutant of the marine environment in Nigeria? A. Insecticides B. Sewage C. Oil D. Inorganic fertilizers |
C |